Gaussian Fitting 함수 C++
Mathematics Algorithm2023. 3. 23. 23:46
반응형
가우시안 피팅을 위한 함수 입니다.
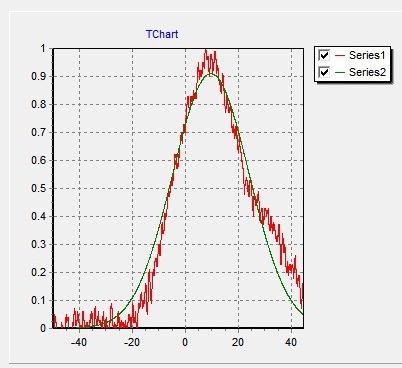
아래 그림에서 붉은색은 측정된 데이타이고 녹색은 가우시안 피팅 데이타 입니다.
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int __fastcall GaussDeviation(double *buf, double *gbuf, int len,
double &peak, double &pkpos, double &pdiam, double &pdev, double base, double cut_level)
{
int i, p1, p2, gbuf_len ;
double pix=0, maxi=0 ;
double sumix = 0, sumi = 0 ; //long type에서 double로 변경, sumi가 0이 되어 gaussianfit하지 않음.
double thresh,thresh1, maxinten ;
double radius=0, center, r2=0., oldr2=0 ;
double *temp ;
temp = max_element(&buf[0], &buf[len]) ;
maxi = *temp ;
//------------ 추가 코드 --------------------
temp = min_element(&buf[0], &buf[len]) ;
base = *temp ;
//-------------------------------------------
maxinten = maxi - base ;
thresh = maxinten * cut_level ;
peak = 0 ;
pkpos = 0 ;
pdiam = 0 ;
pdev = 0 ;
if(len == 0) return 0 ;
for(i=1 ; i<len-1 ; i++)
{
if(buf[i] < thresh) continue ;
pix = buf[i] - thresh ;
sumi += pix ;
sumix += i * pix ;
}
for(p1=1 ; buf[p1]<=thresh && p1<len-1 ; p1++) ; // find first edge
for(p2=len-1 ; buf[p2]<=thresh && p2>p1 ; p2--) ; // find second edge
if(fabs(buf[p1] - thresh) > fabs(buf[p1+1] - thresh)) p1 = p1 + 1 ;
if(fabs(buf[p2] - thresh) > fabs(buf[p2-1] - thresh)) p2 = p2 - 1 ;
center = p1 + (p2 - p1) / 2.0 ;
radius = (p2 - p1 + 1) / 2.0 ;
memset(gbuf, 0, sizeof(double)*len) ;
if(sumi < 1) // If no points, just give center
{
sumix = len / 2 ;
sumi = 1 ;
radius = 0 ;
}
if(sumi >= 1 && radius > 1)
{
double a=0, b=0 ;
if(cut_level > 0)
{
for(i=0 ; i<50 ; i++)
{
GaussianFit(buf,gbuf,len,base,maxinten,radius,center,&a,&b,&r2) ;
maxinten += a ;
radius += b ;
if(r2 < 0.) r2=0. ; // On horrible curves, r2 can go negative!
if(r2<0.005|| (i>1 && a<0.001 && b<0.001)) break ;
if(i>1 && fabs(oldr2-r2)/r2 < .0002) break ; // r2 didn't change
oldr2 = r2 ;
}
}
else
{
for(i=0 ; i<5 ; i++)
{
GaussianFit(buf,gbuf,len,base,maxinten,radius,center,&a,&b,&r2) ;
maxinten += a ;
radius += b ;
if(r2<0.) r2=0. ; // On horrible curves, r2 can go negative!
if(r2<0.005 || (i>1 && a<0.001 && b<0.001)) break ;
if(i>1 && fabs(oldr2-r2)/r2 < .0002) break ; // r2 didn't change
oldr2 = r2 ;
}
}
}
// radius = (p2-p1) / 2. ; // Use the image's radius, not the gaussian's
pdiam = p1 ; //radius*2; 0808..
pdev = r2 ;
peak = maxinten ;
for(i=0 ; i<len ; i++)
{
if(gbuf[i] >= maxinten) pkpos = i ;
}
gbuf_len = p2 - p1 + 1 ;
return gbuf_len ;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
void __fastcall GaussianFit(double *pix, double *gbuf,int npix, double mininten,
double A, double B, double T, double *a, double *b, double *r2)
{
/* pix is the row of pixel data
gbuf is output of fit gaussian
npix is the number of pixels in the row
A is the current amplitude estimate (0 < A < 256)
B is the current width estimate (in pixels)
T is the centroid (assumed to be accurate/constant; 0 < T < npix)
a is the calculated correction for A
b is the calculated correction for B
r2 is the r?goodness-of-fit for the revised estimators
*/
/* note that it would be intuitive for this function to return r2 */
/* SUMMATION VARIABLES */
/* for each pixel : */
double x; /* the distance of the pixel from the centroid = i-T */
double u; /* the partial derivative of the Gaussian estimate w.r.t. A */
double v; /* the partial derivative of the Gaussian estimate w.r.t. B */
double f; /* the current Gaussian estimate */
double F; /* the deviation of the pixel value from the estimate */
/* overall: */
double C=0; /* the sum of u?*/
double D=0; /* the sum of uv */
double E=0; /* the sum of Fu */
double G=0; /* the sum of v?*/
double H=0; /* the sum of Fv */
double J=0; /* the sum of F?*/
/* additional variables from Coherents formulas (without names) */
double sumf=0; /* the sum of revised estimates */
double sumF=0; /* the sum of errors in the revised estimates */
double avgf; /* the average new estimate */
double var; /* the variance between a pixel value and the average */
double sumvar2=0; /* the sum of the squared variances */
int i ;
for(i=0 ; i<npix ; i++) /* this is the slowest part of this function */
{
x = (double)(i-(int)T) ;
f = A * exp(-2.*((x*x)/(B*B))) ; /* (1) */
F = (double)(pix[i]-mininten)-f ; /* (5) */
if(A==0) A = 1 ;
u = f / A ; /* (3) */
if(B==0) B = 1 ;
v = 4.* f *(x*x)/(B*B*B) ; /* (4) */
C += u*u ;
D += u*v ;
E += F*u ;
G += v*v ;
H += F*v ;
J += F*F ;
}
/* new coefficient estimates */
double temp ;
temp = (D*D-C*G) ;
if(temp==0) temp = 1 ;
*b = (E*D-C*H)/ temp ; /* (8) */
*a = -(E*G-D*H)/temp ; /* (9) */
A += *a;
B += *b;
/* analyze estimates using new coefficients */
J = 0 ;
for(i=0 ; i<npix ; i++)
{
x = (double)(i-(int)T) ;
if(B==0) B = 1 ;
f = A*exp(-2.*((x*x)/(B*B))) ;
F = (double)(pix[i]-mininten) - f ;
gbuf[i] = mininten + f ; /* PLOT IDEAL GAUSSIAN */
sumf += f ;
sumF += F ;
J += F*F ;
}
if(npix == 0) npix = 1 ;
avgf = sumf / npix ;
for(i=0 ; i<npix ; i++)
{
var = (double)(pix[i]-mininten) - avgf ;
sumvar2 += var * var ;
}
if(sumvar2==0) sumvar2 = 1 ;
*r2 = 1. - sqrt(J / sumvar2) ;
}반응형
'Mathematics Algorithm' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Data Smoothing #1 알고리즘 C++ (0) | 2023.03.30 |
|---|---|
| Data Smoothing #2 (Savitzky Golay) C++ (0) | 2023.03.30 |
| C# 유전 알고리즘을 적용한 최적의 길찾기 (1) | 2023.03.14 |
| Least Square(최소 자승법) (2) | 2023.02.26 |
| Data Smoothing #3 ( Exponential ) C++ (0) | 2023.02.06 |
댓글()